Artificial Intelligence is one of the most transformative technologies of modern times. It offers remarkable opportunities for businesses and society alike. Yet, alongside these benefits, cybercriminals are increasingly using AI to develop more sophisticated and scalable attacks.
This article explores how AI is being used to augment cybercrime, how it works in practice, and what steps you can take to protect your organisation in an evolving threat environment.
What is AI hacking?
Throughout this article, the term ‘AI hacking’ refers to cybercriminals using AI tools to conduct or enhance attacks. It is worth noting that hacking also has a positive meaning: ethical hackers or ‘white-hat’ hackers use their skills to expose vulnerabilities and strengthen systems. However, the focus here is on malicious use of AI by attackers to further their criminal activities.
AI-enhanced cybercrime has become a significant concern. In recognition of its risks, the UK Government has issued a detailed report outlining its potential dangers and risks to national and organisational security.
Types of AI hacking
Here’s a number of AI hacking threats to look out for:
Deepfake AI hacking
Deepfake tactics use AI-generated video and audio that look like trusted figures to trick people into parting with money or confidential information. For example, an employee of London-based Arup was scammed into transferring $25 million to hackers after attending a video call where deepfake technology was used to mimic the company’s CEO.
AI hacking also uses AI-generated video content, voice recordings and images to spread deepfake propaganda and misinformation that could cause major reputational damage to a business or individual. This is worlds away from genuine deepfakes that use generative AI and facial manipulation of celebrities, politicians, and other well-known figures to promote good causes, such as the A World Without Malaria campaign featuring David Beckham.
Phishing AI hacking
Phishing is another common form of cyber attack that’s used in conjunction with AI hacking. It typically involves sending emails and messages that appear to be from legitimate sources to employees and individuals. The aim is to dupe them into revealing sensitive information or personal details such as passwords and credit card numbers.
Nowadays, AI has enhanced phishing attacks by creating highly personalised, auto-generated emails that appear like they come from senior business leaders and are more legitimate and convincing than ever before. This automation reduces the cost of attacks, has a higher success rate, and remains a popular tactic of hackers. Training your employees to spot a phishing email could save a business huge sums of money and avoid reputational damage.
Malware AI hacking
Adaptable malware that changes and mutates its source code to avoid security detections and gain unauthorised access to networks and devices may sound like science fiction. But AI hacking involves precisely this, and it can be difficult to defend against using traditional antivirus systems that rely on signature-based identification.
Even though most platforms prevent the generation of AI malware, some dark AI sites still offer it as a means of stealing data, disrupting operations, and demanding ransoms from businesses and individuals.

Brute force AI attacks
AI hacking includes brute force attacks where hackers use automated tools to crack passwords, encryption keys, or other security features to gain unauthorised access to networks and systems.
AI brute force attacks are fully automated, so they try every possible password combination and allow hackers to analyse patterns and behaviours and guess passwords faster than manual attacks.
AI social engineering
Hackers use AI to create automated and convincing social engineering scams to dupe people and gain access to confidential information.
These attacks exploit human psychology and con employees and individuals into giving out their private credentials or handing over valuable data by clicking on suspicious links and attachments. AI has enabled hackers to refine and automate these scams, making them more believable and effective than ever before.
AI keystroke hacking
Have you ever typed on your computer with the microphone on during a work conference call? You could become a victim of AI keystroke hacking.
When you type into a device’s keyboard, some AI tools can actually ‘listen’ to your keystrokes and record the different sounds and patterns. This has the potential to allow hackers to steal your passwords with a high degree of accuracy and access your personal data.
AI voice cloning hacking
Like video deepfakes, AI voice cloning is also a dangerous tool in the hands of cybercriminals. Many devices use voice biometrics as a security feature, but hackers also use it for their own malicious purposes.
AI can closely mimic voice recordings and copy audio clips with incredible accuracy. While this can be used for positive outcomes, it also leaves voice-protected systems vulnerable. For instance, users may wrongly believe an audio file came from a legitimate source as opposed to a hacker.
AI CAPTCHA hacking
CAPTCHA has long been used to differentiate humans from bots online, typically creating a challenge such as image recognition or distorted text that humans can easily solve, but machines can’t.
However, AI can now analyse these images and mimic human behaviours, allowing hackers to bypass these challenges. This makes it more difficult to detect automated abuse such as spamming and malicious emails or block unauthorised access to networks and systems.
All of these examples of AI hacking are in use today. And however far-fetched some of them seem, they undoubtedly raise the threat of cybercrime for businesses and individuals.

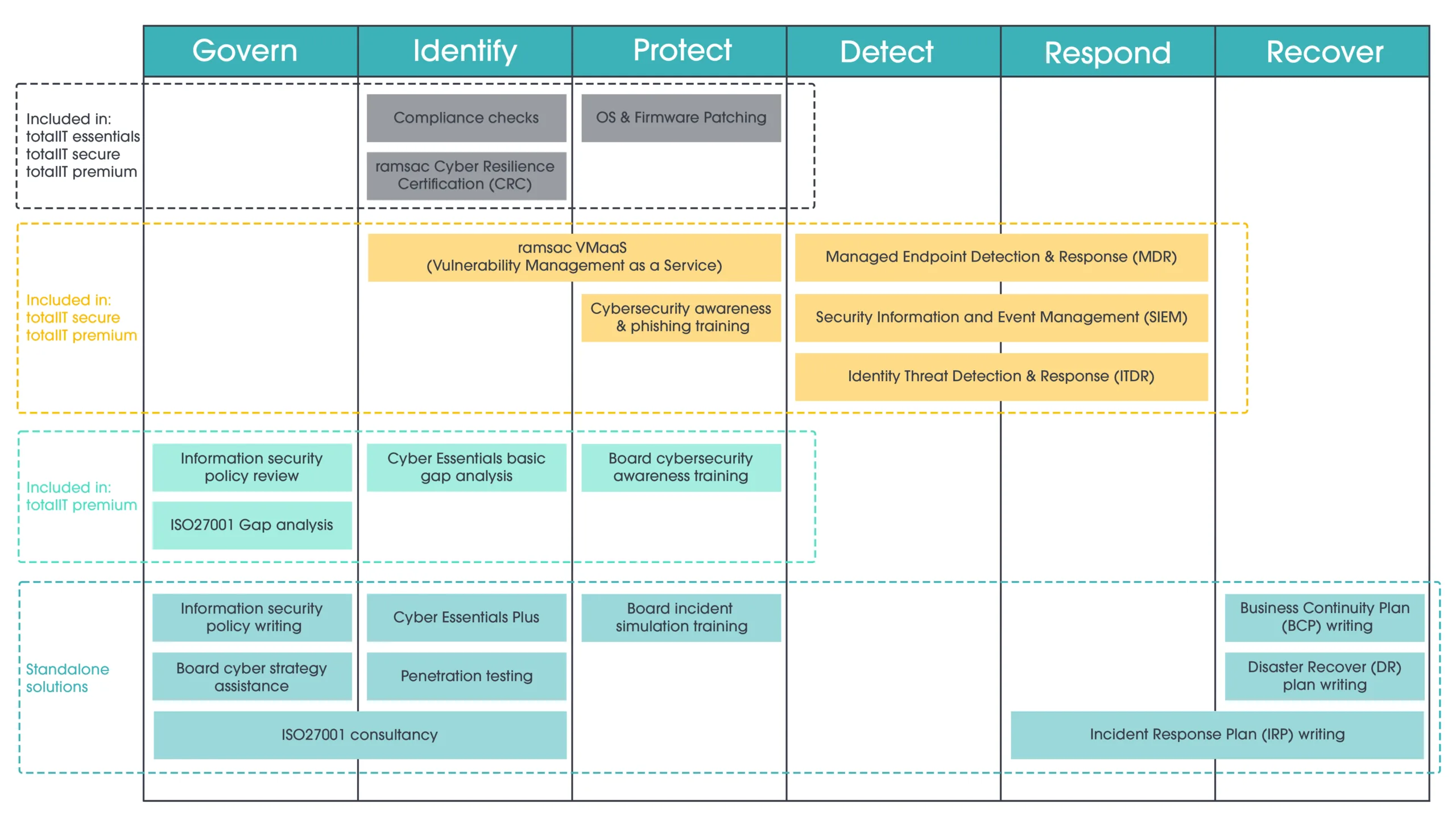
5 ways to protect yourself against AI hacking
With hackers actively using AI to target businesses and individuals, understanding how to protect yourself is vitally important.
To reduce the threat risk within your organisation or home, the following tips will help you minimise your chances of becoming a victim of AI hacking.
1. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) should be a key part of your cybersecurity strategy in the fight against AI hacking. It means users, especially those accessing financial platforms, must provide at least two forms of identification to log into an account or access confidential information.
Examples of MFA include a combination of one-time passwords, authenticator apps, and biometric facial scans for extra security. Therefore, should a hacker breach your password security, they still can’t access your accounts, data, and money.
2. Adopt strong password protocols
Password security was an issue long before AI hacking became a concern. Whether you’re a business or home user, understanding password best practice can help protect your systems from cybercriminals.
Typically, passwords should be more than 15 characters in length and include a combination of letters, numbers and symbols. Similarly, never use the same password for different platforms and accounts. If you can’t remember your passwords use a password manager and never save them in your browser for convenience. Strong passwords are crucial for everyone’s online security.
3. Protect your system and network
Antivirus software was once a standard security feature on every computer in the office and home. Nowadays, a virtual private network (VPN) has become just as important in any AI cybersecurity strategy.
A VPN allows you to conceal your IP address and encrypt data for private and secure browsing. It allows businesses to safeguard their IP address and ensure it isn’t shared with others to minimise risk. Not only will it prevent blocklisting, but it reduces CAPTCHAs and enables secure access to commercial servers.
4. Secure your mobile device usage
Excessive use of mobile devices can leave you vulnerable to AI hacking. Cybercriminals know we can spend too much time on social media or scrolling through platforms, and they’ll use this to their advantage to hack into your accounts.
AI hackers lure their victims by creating fake hotspots with free Wi-Fi that tempt people to join, giving them access to mobile phone data. Therefore, it’s vital to follow secure mobile device management protocols such as using a VPN and disabling Wi-Fi auto-connect settings. You could also activate the setting that allows you to remotely wipe your phone if it gets stolen and always store any personal data in the cloud rather than on the device itself.
5. Install the latest security updates
Avoid any software vulnerabilities in your organisation by ensuring all devices connected to your network stay updated with the latest version. This includes everything from the apps you may have installed to the operating system itself.
To make this process easier, turn on auto-updates on all computers and devices so that security patches will be automatically applied without the hassle of manual updates. This ensures any security gaps are immediately filled to prevent AI hackers accessing your devices.
Are you worried about the risk of AI hacking?
The integration of AI into cybercriminal activity is not a future threat, it is a reality today. However, businesses that stay vigilant, adopt layered security practices, and invest in user education will remain well-positioned to mitigate these risks.
At ramsac, our secure+ cybersecurity monitoring services protect your company from the growing threat of AI hacking. As an award-winning AI consultancy, we’ll enhance your online security and ensure you’ll always be one step ahead of cybercriminals. Contact us today.